True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
When an atom loses electrons, its radius gets smaller.
|
|
|
2.
|
Although the precise location of an electron cannot be determined, it is
possible to determine the probability that an electron will occupy a certain region around the
nucleus.
|
|
|
3.
|
An atom that gains an electron will form a positive ion.
|
|
|
4.
|
As the amount of energy carried by a wave decreases, its wavelength
increases.
|
|
|
5.
|
The electronegativity of elements increases from left to right and from top to
bottom on the periodic table.
|
|
|
6.
|
Elements in the same family tend to have the same number of valence
electrons.
|
|
|
7.
|
Valence electrons refers to the total number of electrons that exist in
the orbitals that occupy the outermost energy level of an atom.
|
|
|
8.
|
The unit for measuring the energy of a wave is Hertz (1/sec).
|
|
|
9.
|
The maximum number of allowed valence electrons in any atom is 8.
|
|
|
10.
|
Six electrons can exist in a p-orbital.
|
|
|
11.
|
The radius of an atom is defined as half the distance between the nuclei of two
adjacent or bonded atoms of that element.
|
|
|
12.
|
The number of electrons in an orbital depends on the orbital’s
shape.
|
|
|
13.
|
[Kr]5s24d105p5 is the correct
electron configuration for the element Bromine, Br.
|
|
|
14.
|
An element can be identified by the characteristic bright-line atomic emission
spectrum it can produce.
|
|
|
15.
|
An p orbital is in the shape of a dumbbell.
|
|
|
16.
|
The photoelectric effect describes the emission of electrons from a
metal’s surface when light at a specific frequency shines on it.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
17.
|
A photon is emitted from an atom with an energy of 4.25 x 10-19 J.
What is the wavelength of the photon?
a. | 273 nm | b. | 425 nm | c. | 642 nm | d. | 467
nm |
|
|
|
18.
|
What is the frequency of a light wave with a wavelength of 680 nm? (convert to
meters first!)
a. | 2.04 s | c. | 4.41 x 1014 Hz | b. | 2.04 x
109 Hz | d. | 2.27 x
10-15 Hz |
|
|
|
19.
|
Which type of orbital is shown? 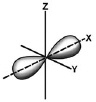
|
|
|
20.
|
Emission of light from an atom occurs when an electron
a. | jumps from a lower to a higher energy level. | b. | moves within its
atomic orbital. | c. | drops from a higher to a lower energy level. | d. | falls into the
nucleus. |
|
|
|
21.
|
How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the
nucleus?
a. | It decreases. | b. | It doubles. | c. | It stays the same. | d. | It
increases. |
|
|
|
22.
|
Which is the correct number of valence electrons in the element Gallium
(Ga)?
|
|
|
23.
|
Which is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from an atom of an
element in the gaseous state? (doesn’t want to give up any!)
a. | ionization energy | c. | electronegativity | b. | law of octets | d. | ionic radius |
|
|
|
24.
|
What is the maximum number of f orbitals in any single energy
level in an atom?
|
|
|
|
|
|
25.
|
Which region contains elements with two valence electrons?
|
|
|
26.
|
Which region contains elements with an electron configuration that ends with
p1?
|
|
|
27.
|
Which of the following factors contributes to the increase in ionization energy
from left to right across a period?
a. | an increase in the shielding effect | b. | fewer electrons in the highest occupied energy
level | c. | an increase in the number of protons, the effective nuclear
charge | d. | an increase in the size of the nucleus |
|
|
|
28.
|
What element in the second period has the largest atomic radius?
a. | potassium | b. | neon | c. | lithium | d. | carbon |
|
|
|
29.
|
When an electron moves from a lower to a higher energy level, the electron
a. | moves closer to the nucleus. | b. | always doubles its energy. | c. | absorbs a quantum of
energy. | d. | absorbs a continuously variable amount of energy. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
30.
|
Which region is referred to as the f-block on the
diagram?
|
|
|
31.
|
Which region is referred to as the s-block on the
diagram?
|
|
|
32.
|
What is the maximum number of d orbitals in a principal energy
level?
|
|
|
33.
|
Which is the correct number of valence electrons in the element Carbon?
|
|
|
34.
|
Which element has the electron configuration
1s22s22p63s23p64s23d4?
|
|
|
35.
|
What types of atomic orbitals are in the third principal energy level?
a. | s and p only | b. | p and d only | c. | s, p, d, and
f | d. | s, p, and d only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
36.
|
Which element has an electron configuration that ends in the fourth energy
level?
|
|
|
37.
|
Which element has full valence shell?
|
|
|
38.
|
The atomic number of an element is the total number of which particles in the
nucleus?
a. | electrons | c. | protons and electrons | b. | protons | d. | neutrons |
|
|
|
39.
|
Which correctly describes elements in the same group?
a. | They must be in the same state of matter. | b. | They have the same
number of valence electrons. | c. | They have the same atomic
radius. | d. | They have electrons in the same outermost energy
level. |
|
|
|
40.
|
The atomic emission spectra of a sodium atom on Earth and of a sodium atom in
the sun would be
a. | the same. | b. | different from each other. | c. | the same as those of
several other elements. | d. | the same as each other only in the ultraviolet
range. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
41.
|
Which diagram correctly depicts the general trend in first ionization
energy?
|
|
|
42.
|
Which diagram correctly depicts the trend in atomic radius?
|
|
|
43.
|
What is the shape of the 3p atomic orbital?
a. | sphere | b. | donut | c. | bar | d. | dumbbell |
|
|
|
44.
|
Each period in the periodic table corresponds to a(n) ____.
a. | orbital | c. | suborbital | b. | principal energy level | d. | sublevel |
|
|
|
45.
|
Identify the period and group numbers of the element with the electron
configuration. [Ne]3s23p4
a. | Period 2, Group 16 | c. | Period 3, Group 4 | b. | Period 3, Group 16 | d. | Period 2, Group
4 |
|
|
|
46.
|
What is the charge of a cation?
a. | a negative charge | b. | a positive charge | c. | no
charge |
|
|
|
47.
|
Which is the most important characteristic in detemining an element’s
chemical properties?
a. | the number of valence electrons it contains | b. | which period it is
found in | c. | its outermost energy level | d. | the number of protons and neutrons in its
nucleus |
|
|
|
48.
|
How does atomic radius change from left to right across a period in the periodic
table?
a. | It tends to decrease. | b. | It tends to increase. | c. | It first decreases,
then increases. | d. | It first increases, then decreases. |
|
|
|
49.
|
Which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius?
|
|
|
50.
|
Which is a transition element with five d-block electrons in energy level
4?
a. | Manganese (Mn) | c. | Technicium (Tc) | b. | Niobium (Nb) | d. | Renium (Re) |
|
|
|
51.
|
What is the electron configuration of potassium, K?
|
|
|
52.
|
What is the maximum number of electrons in the second principal energy
level?
|
|
|
53.
|
What element has the electron configuration 1 s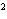 2 s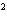 2 p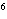 3 s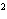 3 p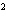 ?
|
|
|
|
|
|
54.
|
Which diagram shows a wave with the highest frequency?
|
|
|
55.
|
How many energy sublevels are in the second principal energy level?
|
|
|
56.
|
Which of the following elements has the smallest first ionization energy?
|
|
|
57.
|
How many half-filled orbitals are in a bromine atom?
|
|
|
58.
|
Which rule for the filling of orbitals in the element Phosphorus is being
violated? 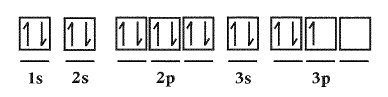 a. | Aufbau Principle | c. | No rules are violated | b. | Hund’s
Rule | d. | Pauli Exclusion
Principle |
|
|
|
59.
|
How does atomic radius change from top to bottom in a group in the periodic
table?
a. | It tends to increase. | b. | It first decreases, then
increases. | c. | It tends to decrease. | d. | It first increases, then
decreases. |
|
|
|
60.
|
What is the maximum number of orbitals in the p
sublevel?
|
|
|
61.
|
Which rule for the filling of orbitals by electrons in the element Magnesium is
being violated? Justify your answer. 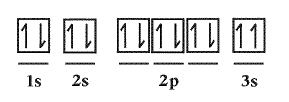 a. | No rules are violated | c. | Hund’s Rule | b. | Aufbau Principle | d. | Pauli Exclusion
Principle |
|
|
|
62.
|
Which of the following statements correctly compares the relative size of an ion
to its neutral atom?
a. | The radius of a cation is identical to the radius of its neutral
atom. | b. | The radius of an anion is identical to the radius of its neutral
atom. | c. | The radius of an anion is greater than the radius of its neutral
atom. | d. | The radius of a cation is greater than the radius of its neutral
atom. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
63.
|
Which label identifies the wavelength of the wave shown?
|
|
|
64.
|
What is the element with the lowest electronegativity value?
|
|
|
65.
|
Which rule is being violated? 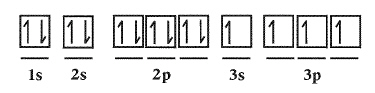 a. | Hund’s Rule | c. | Aufbau Principle | b. | Pauli Exclusion Principle | d. | No rules are
violated |
|
|
|
66.
|
What are quanta of light called?
a. | muons | b. | excitons | c. | photons | d. | charms |
|
|
|
67.
|
What is the element with the highest electronegativity value?
|
|
|
68.
|
How are the frequency and wavelength of light related?
a. | Frequency equals wavelength divided by the speed of light. | b. | Wavelength is
determined by dividing frequency by the speed of light. | c. | They are directly
proportional to each other. | d. | They are inversely proportional to each
other. |
|
|
|
69.
|
Use Plank’s constant, h= 6.626 ´ 10-34, to solve the
following:
What is the amount of energy carried by a photon that has a frequency(v) of 5.71 x
1014 Hz?
E=hv
a. | 525 nm | c. | 1.14 x 10-8 J | b. | 3.78 x
10-19 J | d. | 8.62 x
1047 J/s |
|
|
|
70.
|
What is the next atomic orbital in the series 1s, 2s, 2p,
3s, 3p, 4s?
|