Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
A(n) ____ chemical equation has the same number of atoms of each element on each
side of the equation.
a. | unbalanced | b. | complex | c. | simple | d. | balanced |
|
|
|
2.
|
What is the whole number that appears in front of a formula in a chemical
equation?
a. | a subscript | b. | a coefficient | c. | a ratio | d. | a
superscript |
|
|
|
3.
|
Which equation is not balanced?
a. | 2H2 + O2 ® H2O | c. | 4H2 +
2O2 ®
4H2O | b. | 2H2 + O2 ®
2H2O | d. | H2 + H2 + O2 ® H2O +
H2O |
|
|
|
4.
|
The coefficients in a chemical equation represent the
a. | number of each atom in each compound in a reaction. | b. | relative numbers of
moles of reactants and products. | c. | number of valence electrons involved in the
reaction. | d. | masses, in grams, of all reactants and products. |
|
|
|
5.
|
Each substance to the right of the arrow in a chemical equation is a(n)
____.
a. | reactant | b. | catalyst | c. | inhibitor | d. | product |
|
|
|
6.
|
Which observations indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred?
a. | production of a gas | c. | all of the above | b. | formation of a precipitate | d. | evolution of heat and
light |
|
|
|
7.
|
In writing a chemical equation that produces hydrogen gas, the correct
representation of hydrogen gas is
|
|
|
8.
|
According to the law of conservation of mass, the total mass of the reacting
substances is
a. | sometimes more and sometimes less than the total mass of the
products. | b. | always less than the total mass of the products. | c. | always equal to the
total mass of the products. | d. | always more than the total mass of the
products. |
|
|
|
9.
|
In what kind of reaction do two or more substances combine to form a new
compound?
a. | ionic reaction | c. | synthesis reaction | b. | double-replacement reaction | d. | decomposition
reaction |
|
|
|
10.
|
The reaction, performed in lab, represented by the equation:
Zn(s) +
2HCl(aq) ®
H2 + ZnCl2(aq) is a
a. | decomposition reaction. | c. | double-replacement
reaction. | b. | single-replacement reaction. | d. | composition
reaction. |
|
|
|
11.
|
The reaction, performed in lab, represented by the equation:
2Mg(s) +
O2(g) ® 2MgO(s) is a
a. | decomposition reaction. | c. | double-replacement
reaction. | b. | single-replacement reaction. | d. | synthesis
reaction. |
|
|
|
12.
|
The reaction, performed in lab, represented by the equation:
C25H52 + 38O2 ® 25CO2 + 26H2O is
a(n)
a. | synthesis reaction. | c. | decomposition reaction. | b. | single-replacement
reaction. | d. | combustion
reaction. |
|
|
|
13.
|
The reaction, performed in lab, represented by the equation:
Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2NaI(aq) ® PbI2¯ + 2NaNO3(aq) is a
a. | double-replacement reaction. | c. | decomposition
reaction. | b. | combustion reaction. | d. | synthesis reaction. |
|
|
|
14.
|
The reaction, performed in lab, represented by the equation:
2H 2O 2( aq) 
2H 2O( l) + O 2 is a(n) a. | single-replacement reaction. | c. | decomposition
reaction. | b. | double-replacement reaction. | d. | synthesis
reaction. |
|
|
|
15.
|
What are the correct coefficients when this equation is balanced?
___K
+ ___Br2 ® ___KBr
a. | 2, 1, 2 | b. | 2, 1, 1 | c. | 1, 1, 1 | d. | 1, 2,
1 |
|
|
|
16.
|
What are the correct coefficients when this equation is balanced?
___Sb + ___O2 ®
___Sb4O6
a. | 10, 5, 1 | b. | 1, 2, 10 | c. | 4, 6, 1 | d. | 4, 3,
1 |
|
|
|
17.
|
Which word equation represents the reaction that produces water from hydrogen
and oxygen?
a. | Water can be separated into hydrogen and oxygen. | b. | Water is decomposed
from hydrogen and oxygen. | c. | H2 + O2 ® water. | d. | Hydrogen plus oxygen yields
water. |
|
|
|
18.
|
Which of the following is the correct skeleton equation for the reaction that
takes place when solid phosphorus combines with oxygen gas to form diphosphorus pentoxide?
|
|
|
19.
|
Rewrite the following word equation as a balanced chemical equation. What is the
coefficient and symbol for fluorine? nitrogen trifluoride  nitrogen  fluorine
|
|
|
20.
|
What do you call a solid substance formed from mixing two aqueous solutions like
shown in this figure? 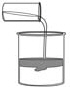 a. | catalyst | b. | synthesis | c. | aqueous | d. | precipitate |
|
|
|
21.
|
In an equation, the symbol for a substance dissolved in water solution is
followed by
a. | (aq). | b. | (1). | c. | (s). | d. | (g). |
|
|
|
22.
|
What does  mean? a. | A catalyst is needed in the reaction. | b. | Heat is supplied to the
reaction. | c. | Electricity is need in the reaction. | d. | A precipitate will form during the
reaction. |
|
|
|
23.
|
A chemical formula written over the arrow in a chemical equation
signifies
a. | an impurity. | c. | the formation of a gas. | b. | a catalyst for the
reaction. | d. | a
by-product. |
|
|
|
24.
|
A catalyst is
a. | the product of a combustion reaction. | b. | speeds up but not used up in a
reaction. | c. | a solid product of a reaction. | d. | one of the reactants in single-replacement
reactions. |
|
|
|
25.
|
A balanced chemical equation allows one to determine the
a. | electron configuration of all elements in the reaction. | b. | energy released in
the reaction. | c. | mechanism involved in the reaction. | d. | mole ratio of any two substances in the
reaction. |
|
|
|
26.
|
In the reaction represented by the equation N2 + 3H2 ® 2NH3,
what is the mole ratio of hydrogen to ammonia?
|
|
|
27.
|
For the reaction represented by the equation C + 2H2 ® CH4,
how many moles of hydrogen are required to produce 1 mol of methane, CH4? (look at
equation)
a. | 4 mol | b. | 0.5 mol | c. | 2 mol | d. | 1
mol |
|
|
|
28.
|
For the reaction represented by the equation 2H2 + O2 ® 2H2O,
how many moles of water can be produced from 6.0 mol of oxygen? (look at equation)
a. | 12 mol | b. | 2.0 mol | c. | 6.0 mol | d. | 18
mol |
|
|
|
29.
|
What is the first step in most stoichiometry problems?
a. | convert given quantities to moles | b. | convert given quantities to
masses | c. | add the coefficients of the reagents | d. | convert given quantities to
volumes |
|
|
|
30.
|
For the reaction represented by the equation 2Na + 2H2O ® 2NaOH + H2, how many grams of hydrogen are produced from 80. g
of water? (3 steps)
a. | 200 g | b. | 45 g | c. | 4.5 g | d. | 80.
g |
|
|
|
31.
|
For the reaction represented by the equation 2H2 + O2
® 2H2O, how many grams of water are produced from 134.4 L
of hydrogen at STP? (3 steps)
a. | 108 g | b. | 54.0 g | c. | 2.00 g | d. | 6.00
g |
|
|
|
32.
|
For the reaction represented by the equation CH4 + 2O2
® CO2 + 2H2O, how many moleculess of carbon
dioxide are produced from the combustion of 100. g of methane?
a. | 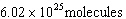 | c. | 37.6 moles | b. | 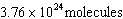 | d. | 100 molecules |
|
|
|
33.
|
A chemical reaction involving substances A and B stops when B is completely
used. B is the
a. | primary product. | c. | limiting reactant. | b. | excess reactant. | d. | primary
reactant. |
|
|
|
34.
|
Which reactant controls the amount of product formed in a chemical
reaction?
a. | excess reactant | c. | composition reactant | b. | limiting reactant | d. | mole ratio |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which statement is true if 12 mol CO and 12 mol Fe 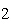 O 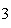 are allowed to react? 3CO( g)
+ Fe 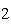 O 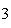 ( s)  2Fe( s) +
3CO 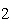 ( g) a. | The limiting reagent is CO and 8.0 mol Fe will be formed. | b. | The limiting reagent
is CO and 3.0 mol CO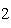 will be formed. will be formed. | c. | The limiting reagent
is Fe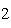 O O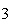 and 24
mol Fe will be formed. and 24
mol Fe will be formed. | d. | The limiting reagent is Fe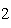 O O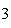 and 36 mol CO and 36 mol CO will be
formed. will be
formed. |
|