Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | mass number | d. | atomic mass | b. | atomic mass unit | e. | isotope | c. | atomic
number |
|
|
|
1.
|
the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
|
|
|
2.
|
the number of protons in the nucleus of an element
|
|
|
3.
|
the average of the masses of the isotopes of an element
|
|
|
4.
|
atoms with the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons in the
nucleus of an atom
|
|
|
5.
|
unit of measurement used to measure an atom’s mass
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | proton | d. | electron | b. | nucleus | e. | neutron | c. | atom |
|
|
|
6.
|
a negatively charged subatomic particle
|
|
|
7.
|
a subatomic particle with no charge
|
|
|
8.
|
a positively charged subatomic particle
|
|
|
9.
|
the central part of an atom, containing protons and neutrons
|
|
|
10.
|
the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that
element
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
|
|
|
11.
|
What is the mass number of the atom shown above?
|
|
|
12.
|
Which is the correct symbol for this atom shown above?
|
|
|
13.
|
Very energetic particles that move in all directions around the nucleus of an
atom are
a. | electrons. | b. | protons. | c. | neutrons. | d. | charges. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Balance the following equation: 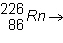 ____ + 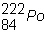
|
|
|
15.
|
The three types of nuclear radiation in order of weakest to strongest are
____.
a. | beta, gamma, alpha | c. | alpha, beta, gamma | b. | alpha, gamma, beta | d. | all of the
above |
|
|
|
16.
|
An atom has 12 protons and 13 neutrons. Which is the correct chemical symbol for
this atom?
|
|
|
17.
|
Which element has 14 protons?
|
|
|
18.
|
Most of the space in an atom is occupied by the
a. | nucleus. | b. | electrons. | c. | neutrons. | d. | protons. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The atomic mass of an element is the average of the masses of its
a. | naturally occurring isotopes. | c. | artificial
isotopes. | b. | radioactive isotopes. | d. | two most abundant isotopes. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Which one(s) have a mass of 1 amu and make up the mass number of an atom?
a. | electron and proton | c. | proton | b. | electron | d. | proton and
neutron |
|
|
|
21.
|
What single dose of radiation will damage human tissue?
a. | 100 radiators | c. | 100 rem | b. | 100 alligators | d. | 1 x 10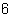 rem
rem |
|
|
|
22.
|
What unit measures radiation damage to human tissue?
a. | liter | b. | rem | c. | meter | d. | half-life |
|
|
|
23.
|
The half-life of a radioisotope is the amount of time it takes for
a. | half of a given sample to decay. | b. | all the sample to decay. | c. | the age of an
artifact to be calculated. | d. | one half of an atom to
decay. |
|
|
|
24.
|
How many electrons are needed to completely fill the second energy level?
|
|
|
25.
|
Neon-22 contains 12 neutrons. It also contains
a. | 22 electrons. | c. | 22 protons. | b. | 12 protons. | d. | 10 protons. |
|
|
|
26.
|
Which is the smallest subatomic particle, (is has nearly no mass at all)
a. | neutron | b. | proton | c. | electron | d. | atom |
|
|
|
27.
|
Each inner energy level of an atom has a maximum number of ____ it can
hold.
a. | electrons | b. | neutrons | c. | protons | d. | quarks |
|
|
|
28.
|
Which of the following is not part of Dalton's atomic theory?
a. | All matter is composed of extremely small particles called atoms. | b. | Atoms of one element
cannot be changed into atoms of another element | c. | In chemical reactions, atoms combine in whole
number ratios.. | d. | The number of protons in an atom is its atomic
number. |
|
|
|
29.
|
What does the 256 in mendelevium-256 represent? (Md=mendelevium)
a. | the neutron number | c. | the atomic number | b. | the mass number | d. | the electron
number |
|
|
|
30.
|
During radioactive decay, the nucleus disintegrates into
a. | a lighter and more stable nucleus. | c. | a heavier and less stable
nucleus. | b. | a heavier and more stable nucleus. | d. | a lighter and less stable
nucleus. |
|
|
|
31.
|
Which best describes Dalton's model of the atom?
a. | a positive mass containing electrons scattered throughout. | b. | a positive center
surrounded by electrons. | c. | a tiny solid sphere that cannot be split into
smaller parts. | d. | a nuclues containing protons and neutrons surrounded by
electrons. |
|
|
|
32.
|
Which of these particles has a mass about equal to a neutron?
a. | proton | b. | electron | c. | nucleon | d. | atom |
|
|
|
33.
|
Which scientist described a positively charged core (“nucleus”) in
the middle of a lot of empty space?
a. | Bohr | b. | Thomson | c. | Rutherford | d. | Chadwick |
|
|
|
34.
|
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of
_________.
a. | charges. | b. | protons. | c. | electrons. | d. | neutrons. |
|
|
|
35.
|
Which scientist described the existence of the neutron?
a. | Thomson | b. | Chadwick | c. | Rutherford | d. | Bohr |
|
|
|
36.
|
What does the 101 in 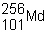 represent? a. | the mass number | c. | the atomic number | b. | the number of neutrons | d. | the nuclide
number |
|
|
|
37.
|
Thorium-234 has a half-life of 24 days. If you started with a 100-g sample of
thorium-234, how much would remain after 48 days?
a. | 25 g | b. | 100 g | c. | 50 g | d. | 10 g |
|
|
|
38.
|
What is the greatest number of electrons an atom can have in the third energy
level?
|
|
|
39.
|
The type of radiation that can be stopped by a sheet of paper is ____
radiation.
|
|
|
40.
|
Which is the number of neutrons in 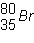 ?
|