True/False - Indicate whether the statement is true [a] or
false [b].
|
|
|
1.
|
If the atomic mass of a manganese atom is 54.94 amu, then its molar mass is
54.94 g/mol.
|
|
|
2.
|
One mole of a substance has the same number of particles as one mole of any
other substance, regardless of what substances are being compared.
|
|
|
3.
|
One mole of a substance has the same volume as one mole of any other substance,
regardless of what substances are being compared.
|
|
|
4.
|
Molarity is the number of moles of solute dissolved per liter of solution
|
|
|
5.
|
Avogadro’s number refers to the number of particles in one gram of a
substance.
|
|
|
6.
|
The empirical formula for a compound consists of the symbols for the elements in
the compound without any subscripts.
|
|
|
7.
|
An element’s molar mass is equivalent to the atomic number of the
element.
|
Matching
|
|
|
Match each item with the correct statement below. a. | representative particle | c. | Avogadro's
number | b. | mole | d. | standard temperature and pressure |
|
|
|
8.
|
the number of representative particles of a substance present in 1 mole of that
substance
|
|
|
9.
|
an atom, a formula unit, or a molecule, depending upon the way a substance
commonly exists
|
|
|
10.
|
the SI unit used to measure amount of substance
|
|
|
11.
|
0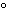 C and 1 atm C and 1 atm
|
Multiple Guess!!-Select the best answer for each question or
problem.
|
|
|
12.
|
Which of the following elements exists as a diatomic molecule?
a. | neon | b. | lithium | c. | nitrogen | d. | sulfur |
|
|
|
13.
|
The formula for carbon dioxide, CO2, can represent
a. | one molecule of carbon dioxide. | b. | 1 mol of carbon dioxide
molecules. | c. | the combination of 1 atom of carbon and 2 atoms of oxygen. | d. | all of the
above. |
|
|
|
14.
|
All of the following are equal to Avogadro's number EXCEPT ____.
a. | the number of atoms of gold in 1 mol Au | b. | the number of atoms
of bromine in 1 mol Br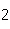 | c. | the number of molecules of nitrogen in 1 mol
N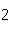 | d. | the number of molecules of carbon monoxide in 1
mol CO |
|
|
|
15.
|
For which of the following conversions does the value of the conversion factor
depend upon the formula of the substance?
a. | volume of gas (STP) to moles | b. | density of gas (STP) to molar
mass | c. | mass of any substance to moles | d. | moles of any substance to number of
particles |
|
|
|
16.
|
The volume of one mole of a substance is 22.4 L at STP for all ____.
a. | gases | b. | liquids | c. | solids | d. | compounds |
|
|
|
17.
|
What is the formula mass of ethyl alcohol, C2H5OH?
a. | 30.33 amu | b. | 33.27 amu | c. | 45.06 amu | d. | 46.08
amu |
|
|
|
18.
|
How many oxygen atoms are there in 0.500 mol of CO2?
a. | 6.02 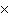 1023 1023 | b. | 3.01 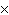 1023
1023 | c. | 15.9994 | d. | 11.0 |
|
|
|
19.
|
How many moles of calcium are in 425 g calcium (Ca)?
a. | 10.6 mol | c. | 171 mol | b. | 70.5 mol | d. | 255 mol |
|
|
|
20.
|
How many molecules are there in 5.0 g of methyl alcohol,
CH3OH?
a. | 9.4 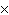 1022 1022 | b. | 3.0 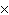 1024
1024 | c. | 3.6 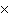 1024 1024 | d. | 3.8 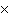 1024
1024 |
|
|
|
21.
|
Calculate the number of molecules in 4.0 mol H2O.
a. | 0.60 x 1023 molecules | c. | 2.4 x 10–23
molecules | b. | 2.4 x 1024 molecules | d. | 2.4 x 1023
molecules |
|
|
|
22.
|
What is true about the molar mass of chlorine gas?
a. | The molar mass is 35.5 g. | b. | The molar mass is 71.0 g. | c. | The molar mass is
equal to the mass of one mole of chlorine atoms. | d. | none of the
above |
|
|
|
23.
|
Given 1.00 mole of each of the following gases at STP, which gas would have the
greatest volume?
a. | He | b. | O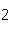 | c. | SO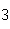 | d. | All are
equal. |
|
|
|
24.
|
What is the percent composition of carbon, in heptane, C 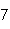 H 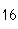 ?
|
|
|
25.
|
The percentage composition of sulfur in SO2 is about 50%. What is the
percentage of oxygen in this compound?
|
|
|
26.
|
The lowest whole-number ratio of the elements in a compound is called the
____.
a. | empirical formula | c. | binary formula | b. | molecular formula | d. | representative
formula |
|
|
|
27.
|
A molecular compound has the empirical formula XY3. Which of the
following is a possible molecular formula?
|
|
|
28.
|
Which of the following is NOT an empirical formula?
|
|
|
29.
|
What is the empirical formula for a compound that is 43.6% phosphorus and 56.4%
oxygen?
|
|
|
30.
|
A compound contains 64 g of O and 8 g of H. What is the empirical formula for
this compound?
|
|
|
31.
|
A compound's empirical formula is N2O5. If the
formula mass is 108 amu, what is the molecular formula?
|
|
|
32.
|
A compound's empirical formula is CH. If the formula mass is 52 amu, what
is the molecular formula?
|
|
|
33.
|
What is the empirical formula of a compound that is 40% sulfur and 60% oxygen by
weight?
|
|
|
34.
|
Which of the following does not increase the rate of dissolving a solid
in water?
a. | raising the temperature of the water | b. | stirring the solution | c. | using larger pieces
of solid | d. | crushing the solid |
|
|
|
35.
|
In a concentrated solution there is ____.
a. | no solvent | c. | a small amount of solute | b. | a large amount of
solute | d. | no
solute |
|
|
|
36.
|
Two liquids that can be mixed together but separate shortly after are:
a. | immiscible | b. | insoluble | c. | miscible | d. | soluble |
|
|
|
37.
|
What is the molarity of a solution that contains 0.202 mol KCl in 7.98 L
solution?
a. | 0.0132 M | b. | 0.0253 M | c. | 0.459 M | d. | 1.363
M |
|
|
|
38.
|
What is the molarity of a solution that contains 125 g NaCl in 4.00 L solution?
(molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g/mol)
a. | 0.535 M | b. | 2.14 M | c. | 8.56 M | d. | 31.3
M |
|
|
|
39.
|
What is the molarity of a solution that contains 6 moles of solute in 2 liters
of solution?
|
|
|
40.
|
Which of the following operations yields the number of moles of solute?
a. | molarity 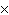 moles of solution moles of solution | c. | molarity 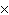 mass of
solution mass of
solution | b. | molarity 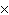 liters of solution liters of solution | d. | moles of solution 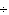 volume of
solution volume of
solution |
|
|
|
41.
|
What mass of Na 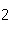 SO 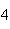 is needed to make 2.5 L of
2.0 M solution? (Na = 23 g; S = 32 g; O = 16 g) a. | 178 g | b. | 284 g | c. | 356 g | d. | 710
g |
|
|
|
42.
|
Which of the following is NOT true about empirical and molecular
formulas?
a. | The molecular formula of a compound can be the same as its empirical
formula. | b. | The molecular formula of a compound can be some whole-number multiple of its
empirical formula. | c. | Several compounds can have the same empirical
formula, but have different molecular formulas. | d. | The empirical formula of a compound can be
triple its molecular formula. |
|